Vacuum forming
$0.00
Vacuum forming is a process in which the plastic sheet becomes soft and flexible during different stages. It is heated and by creating air pressure and vacuum, the softened sheet sits on the mold and takes the shape of the mold.
5) Printing and Related Industries Projects
- H) Vacuum Forming (Plastic):
Vacuum forming (plastic) is a process where a plastic sheet becomes soft and flexible through various stages, is heated, and then conforms to the shape of a mold by applying pressure.
Vacuum forming (plastic) is used for packaging with a desired shape (indentations and protrusions), which is produced and manufactured using thermal molds. There are two types of plastic packaging: lead and CNC mold.
The New World of Design, Printing, and Advertising offers vacuum forming for various electronic products such as memory cards, USB flash drives, laboratory products, toy packaging, and egg packaging, as well as printed vacuum-formed egg packaging in three sizes: small, medium, and large, with the best quality and at the lowest price for the first time in Iran. The materials used in vacuum forming (plastic) include ABS, HP, PET, and PVC.
In the vacuum forming (plastic) process, plastic sheets are softened and made flexible, then heated with a special machine. The air between the sheet and the mold is then vacuumed out using a pump, and the heated plastic sheet is placed on the cooled mold to take shape.
Vacuum forming (plastic) is used for packaging many products, such as food packaging, sweets, toys, cosmetics, automotive parts, and even egg packaging.
Applications of Vacuum Forming:
This process has many uses and applications, some of which include:
Packaging in Industry:
Vacuum forming is used in packaging toys, electronic devices, sweets, chocolates, and other items.
Vacuum Forming in Agriculture:
In agriculture, it is used to make agricultural trays, pots, and domed greenhouses.
Hospital Supplies and Vacuum Forming:
In hospitals, vacuum molds are used for packaging ampoules, medicines, and medical supplies.
Household Items and Vacuum Molds:
Vacuum molds can be seen in household and kitchen items such as spoon and fork holders and kitchen organizers.
Signage Industry and Vacuum Mold Design:
In the sign-making profession, vacuum molds are used to create raised letters and shapes for signs. Vacuum forming molds are also used in the automotive industry and electronic services.
Types of Vacuum Forming:
- A) One-Piece Vacuum Forming:
In one-piece vacuum forming, the item is placed inside the vacuum-formed plastic, and then the vacuum-formed item is placed inside a box or on cardboard and packaged. It should be noted that if cardboard is used underneath the vacuum-formed plastic, there are four methods to secure the plastic and cardboard together.
دستگاه بسته بندی وکیوم فرمینگ ( ویدئو )
https://pack.dn-24.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/وکیوم-فرمینگ-1.mp4
What is Vacuum Forming Packaging? + 6 Common Types
Vacuum forming is a method used to shape plastic sheets.
In this process, a plastic sheet is first placed over a mold, which can be made of metal or wood. Then, the sheet is heated until it becomes soft and flexible.
Once the sheet is soft and pliable, a vacuum pump is used to remove the air between the sheet and the mold, creating a vacuum. This causes the plastic sheet to conform to the shape of the mold.
Finally, after the plastic sheet has cooled down, it can be removed from the mold, resulting in a plastic piece that has taken the shape of the mold. This process, which is widely used in the packaging industry, is known as vacuum forming.
Vacuum Forming Steps (6 Steps)
Clamping: The plastic sheet is placed on a frame. The clamps must be strong enough to hold the plastic sheet securely during the forming process.

- Heating: Heat is applied to the plastic sheet using a heater until it reaches the desired temperature and becomes soft and flexible. The heat must be applied evenly to the plastic sheet.
- Vacuuming: The frame holding the softened plastic sheet is lowered onto the mold. Air is then evacuated, creating a vacuum that pulls the sheet into place. Plastic sheets attached to male molds do not require any additional work at this stage, but plastic sheets attached to female molds usually need small holes in the grooves. This allows the vacuum to shape the sheet into the desired form with high detail.
- Cooling: Fans are sometimes used at this stage to speed up the cooling of the plastic sheet, especially when larger products are being made.
- Demolding: The cooled plastic is removed from the mold and released from the frame. The plastic must be completely cooled before this step; if released too soon, the product may become deformed.
- Trimming: Any excess material is cut, removed, or sanded from the shaped sheet to make it completely smooth. This stage may also involve punching holes, creating grooves, or making cuts in the product if needed. Once this step is complete, the product can move on to the final production stages (design, etc.) or be prepared for final sale.
6 Common Types of Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming with a Female Mold

The most common vacuum forming method uses a concave or female mold, where atmospheric pressure shapes the softened plastic sheets over the mold.
This type of vacuum forming is only suitable for products with shallow depths. Products with excessive depth can cause the plastic sheet to stretch too much, resulting in an asymmetrical and uneven final product, and may sometimes lead to a very thin base.
2- Vacuum forming with male mold

Vacuum forming with a convex or male mold is an excellent option for moldings that require high precision in dimensions, such as thin-walled plastic parts with convex and raised shapes. In this method, the softened plastic is stretched over the mold, forming the inside of the object.
Due to its ability to produce thin-walled plastic parts with precise, sharp, and smooth edges, this method is used for various applications, including packaging, displays, and industrial model-making.
3- Vacuum forming with male and female molds at the same time

To perform this process, the plastic sheet is first heated until it becomes soft, and then compressed air is blown through the mold to inflate the plastic sheet.
Next, the mold is lowered onto the inflated sheet, and the sheet is vacuumed into the mold. At the same time, compressed air is pumped into the female mold, pressing the plastic sheet against the outer surface of both molds to shape it.
This vacuum forming method is used for shaping plastic parts with deep cavities.
Since the soft plastic sheet is inflated and stretched before forming, the sheet maintains a relatively uniform thickness.
4- Vacuum forming with the help of a blower (inflatable)

For parts that require walls with uniform thickness, plastic sheets that have been fully heated and softened are placed in a warm vacuum chamber. Then, using a blower, compressed air is blown into the sheet, inflating it like a balloon.
After inflation, the desired mold is placed under the soft, inflated sheet, and air is immediately evacuated from the vacuum chamber. Atmospheric pressure causes the sheet to collapse into the mold. Since the plastic sheet is well-stretched around the mold before vacuuming, the final part will have uniform thickness.
This vacuum forming method is used to produce thin-walled plastic parts with precise details, sharp and smooth edges, for various applications, including packaging, displays, and industrial model-making.
5- Vacuum forming with auxiliary male mold (auxiliary plug)

In some molds with greater depth, there is a stage after the stretching phase where a plug assist is used. When a standard vacuum forming machine cannot evenly distribute the plastic sheet over the mold, vacuum forming with a male mold and an assist plug is used.
This plug helps to distribute the molten plastic sheet evenly across the surface of the mold, ensuring that all the voids in the mold are filled. These plugs also help prevent the plastic sheet from thinning out, providing more material to reach the bottom of the mold.
6- Vacuum forming with the help of compressed air and vacuum at the same time

After the plastic sheet is heated, a combination of a piston and compressed air is gently applied to press the sheet.
Next, compressed air is blown around the mold to guide the heated plastic sheet onto the mold. At this point, the sheet is positioned between two layers of air buffer, and the mold gradually lowers.
The compressed air is then released to allow the plastic sheet to form around the mold.
The wall thickness of plastic parts formed using this method is relatively uniform, and deeper plastic parts can be shaped.
Types of Plastic Materials Usable in Vacuum Forming
The table below provides a quick guide to plastics most commonly used in vacuum forming.
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a highly transparent and flexible plastic sheet that is widely used in various applications due to its clarity and durability, including windows, skylights, signage, and vehicles.

| Plastic | Main features | Key features | Common uses |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Acrylic – transparent polymer (PMMA) |
moisture permeable medium/strong Temperature sensitive, may become brittle Shrinkage rate 0.3 – 0.8% Prone to chipping but good for manual work and accepts cellulose sprays and enamels Available in several colors, it can be transparent or opaque |
It is very suitable for applications where transparency is important. |
Lights and diffusers, ceiling domes, restrooms (including bathtubs) and signs |
Lights and diffusers, ceiling domes, restrooms (including bathtubs) and signs
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
A water-insoluble thermoplastic with excellent resistance to chemicals, impact, abrasion, and stress. This plastic is rigid, tough, and stable, with good electrical properties. It is used for making rigid pipes, automotive parts, car wheels, and more.

| Plastic | Key features | Main features | Common uses |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
Strong moisture wicking, easy to shape with great detail Shrinkage rate 0.3-0.8% Cuts fast and easy Accepts all types of colors Infinite color gamut |
It is tough and inflexible, resisting both weather conditions and impact. |
Electrical boxes, luggage, sanitary parts and vehicle parts Polycarbonate (PC) |
Polycarbonate is a plastic polymer used in the manufacturing of many machine parts.
It is a good option because it is nearly unbreakable, highly durable, protected from UV radiation on one or both sides, and is half the weight of glass, making it easy to install and handle in machines.
It is used in light diffusers, skylights, aircraft canopies, and more.

| Plastic | Main features | Key features | Common uses |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Polycarbonate (PC / LEXAN / MAKROLON) |
Moisture-absorbent Very strong Shapes well with high detail Shrinkage rate of 0.6 – 0.8% Can be machined, ultrasonically welded, bonded, drilled, and sprayed Available in transparent, translucent, and solid colors, with textured finishes, colorful patterns, and light-diffusing properties |
It has very good resistance to fire and impact. |
Excellent resistance to fire and impact. Aircraft interior trim, guards/vests/shields, light diffusers, markings and reflectors |
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is a plastic sheet produced from petroleum, known for its high resistance to water and chemicals. It remains highly stable in freezing environments, has a low coefficient of resistance, and is very flexible. Due to its low cost, it is widely used and suitable for almost all environments.

| Plastic | Main features | Key features | Common uses |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Polyethylene (HDPE) |
Very strong moisture repellent PE itself is challenging but PE foam can be easily handled but requires forming at low temperatures Shrinkage rate 2.0 – 3.5% Cannot be sprayed but can be printed with special inks Black, white and color |
It is very similar to PP. It has a high shrinkage rate but good chemical resistance. |
Caravan parts, circles and places, vehicle parts |
Caravan parts, circles and places, vehicle parts
PETG copolyester is a thermoplastic that, in its unaltered form, possesses durability, strength, and resistance to harsh environments. It is used in vacuum forming techniques because it can be easily molded, die-cut, colored, and shaped.
This plastic is highly transparent and is used in the production of food containers, water bottles, toys, and other items.

Plastic |
Main features | Key features | Common uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene terephthalate glycol / polyester copolymer (PETG) | Can usually be used directly without the need for prior drying
Good formability with good detail Shrinkage rate 0.3 – 0.7% Can be sawed, cut and machined. It can be molded and punched to some extent. It can be printed with colors and inks designed for polyester Mostly transparent, limited color range |
Sterilizable and resistant to alcohols and acidic oils, but not recommended for use with alkaline solutions. Attractive and easy to shape. | Sanitary packaging (e.g. for food and pharmaceuticals), displays (e.g. sales displays) |
It is a plastic polymer used in the vacuum forming process as a material for specific objects, such as model making, crafts, and report covers in schools and offices. These sheets are rigid, semi-hard, and have high resistance to heat, fatigue, and chemicals. Additionally, they are crystalline, non-polar, and semi-transparent in appearance.

| Plastic | Main features | Key features | Common uses |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Polypropylene (PP) |
Moisture impervious very strong It is difficult to form. It requires precise control of temperature and sheet surface Shrinkage rate 1.5 – 2.2% Can not be sprayed Clear, available in black, white and color |
Difficult to shape and prone to sagging, but very flexible and non-absorbent. |
Chemical tanks and containers, luggage, packaging for food and medicine, toys High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) |
It is a hard and strong plastic with high impact resistance. This plastic can be easily cut, trimmed and machined and is available in a variety of colors. Therefore, this inexpensive plastic is useful for making toys, signs, and point-of-sale displays.


| Plastic | Main features | Key features |
Common uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Polystyrene (HIPS) |
Moisture impervious
medium/strong It forms well and can accurately capture high detail Shrinkage rate 0.3 – 0.5% It is machined well but needs a special primer to be sprayed Available in clear and colored, patterned and textured forms. |
It has poor resistance to UV rays, so it is best for indoor applications. It is very easy to shape and is available in a wide range of colors, patterns and textures. | Most high volume/low value items such as many (non-sterile) packages.
Samples of products of various industries produced by vacuum forming |
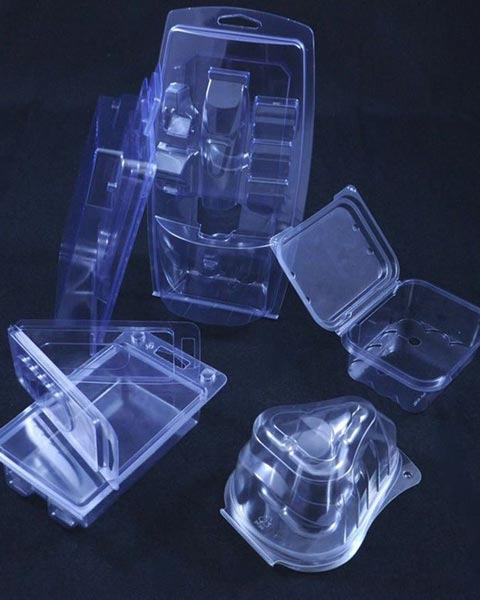
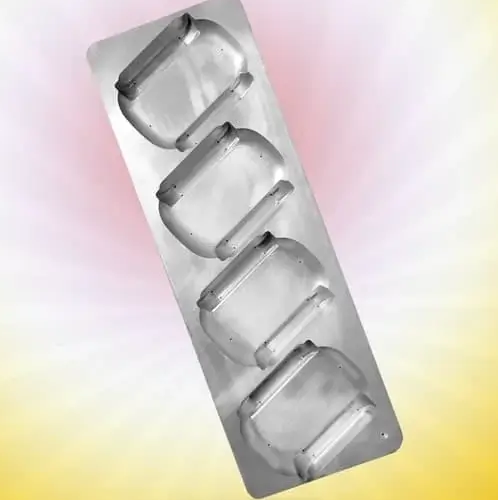
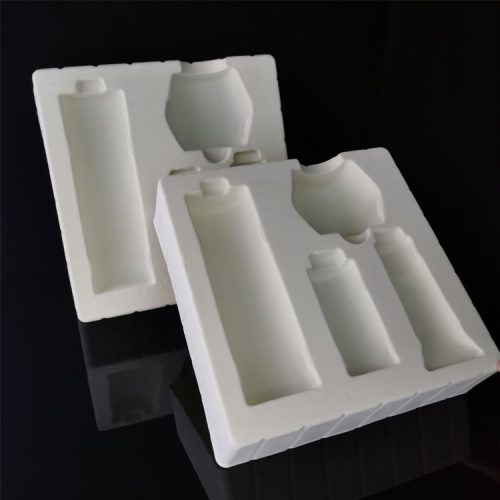


























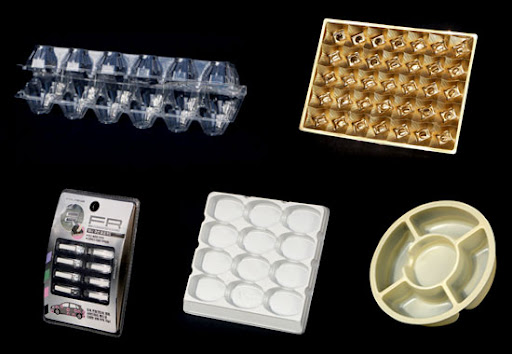















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.