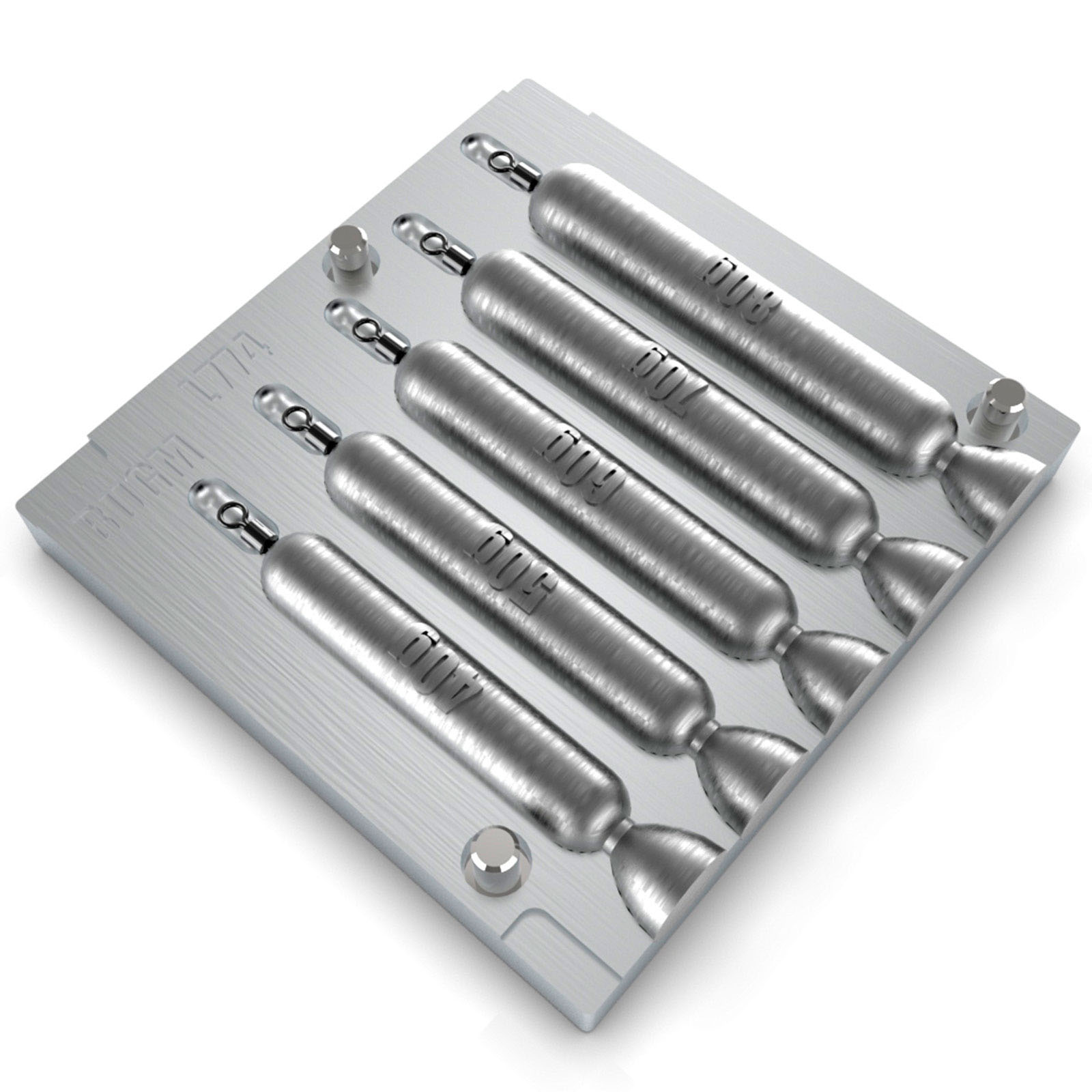
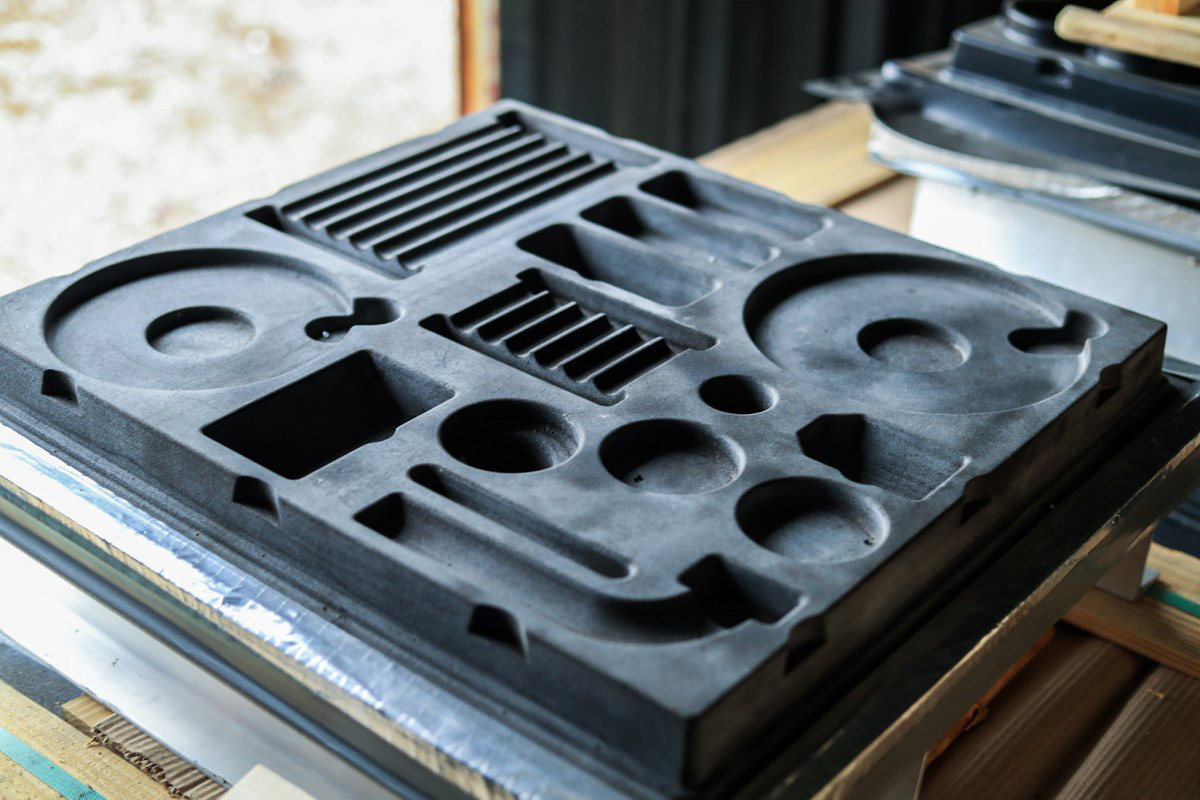
Vacuum forming mold
$0.00
The vacuum forming mold is offered by two methods, CNC and casting, which is more precision CNC and casting is the traditional method.
If you have ever used vacuum forming technology to create plastic parts, you are likely familiar with vacuum forming molds. However, you might find it interesting that these molds can be made using different methods.
Wooden Molds: These are traditional molds made by carving wood or specialized foam. The advantage of wooden molds is that they are strong and durable, capable of being used hundreds or even thousands of times for vacuum forming. However, over time, wood can crack or warp. Therefore, wooden molds are best used when high detail on the final product is not required, or when the thickness of the mold is not crucial.
Aluminum Molds: If you need to produce a large number of parts (over 100,000), cast aluminum molds are the best option. These molds are incredibly strong and durable, making them suitable for long-term production of plastic parts. However, the cost of making these molds is high, and it may take several months to complete them, which makes them uneconomical for small productions.
Structural Foam Molds: These molds are also strong and durable and can be used to produce many parts. Unlike aluminum molds, they are lightweight and cheaper. These molds are made from special plastics that are thickened with specific chemicals, increasing the mold’s lifespan.
A vacuum forming mold is an essential tool used to produce high-quality products. The mold must be made from materials that can withstand the heat and pressure of the vacuum forming process. It must also be made from materials that are compatible with the plastic used for the product.
Molds are usually made from aluminum, steel, or wood. Aluminum is a popular material for molds because it is lightweight and inexpensive. It is also a good heat conductor, which allows it to heat up and cool down quickly. Steel is more durable than aluminum and can withstand more heat and pressure. Wood is cheaper than aluminum and steel but not as durable.
Molds need to be properly designed to ensure a high-quality final product. The mold design must be precise to produce a product with the desired shape and size. It should also be smooth to ensure that the product’s surface is flawless.
Molds should be regularly maintained to perform well. They must be cleaned of any damage or defects. Additionally, they should be lubricated to prevent plastic from sticking to them.
As we have seen, each type of mold has its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the best mold depends on various factors, such as the number of required parts, budget, and details of the final product.
Vacuum Forming Mold
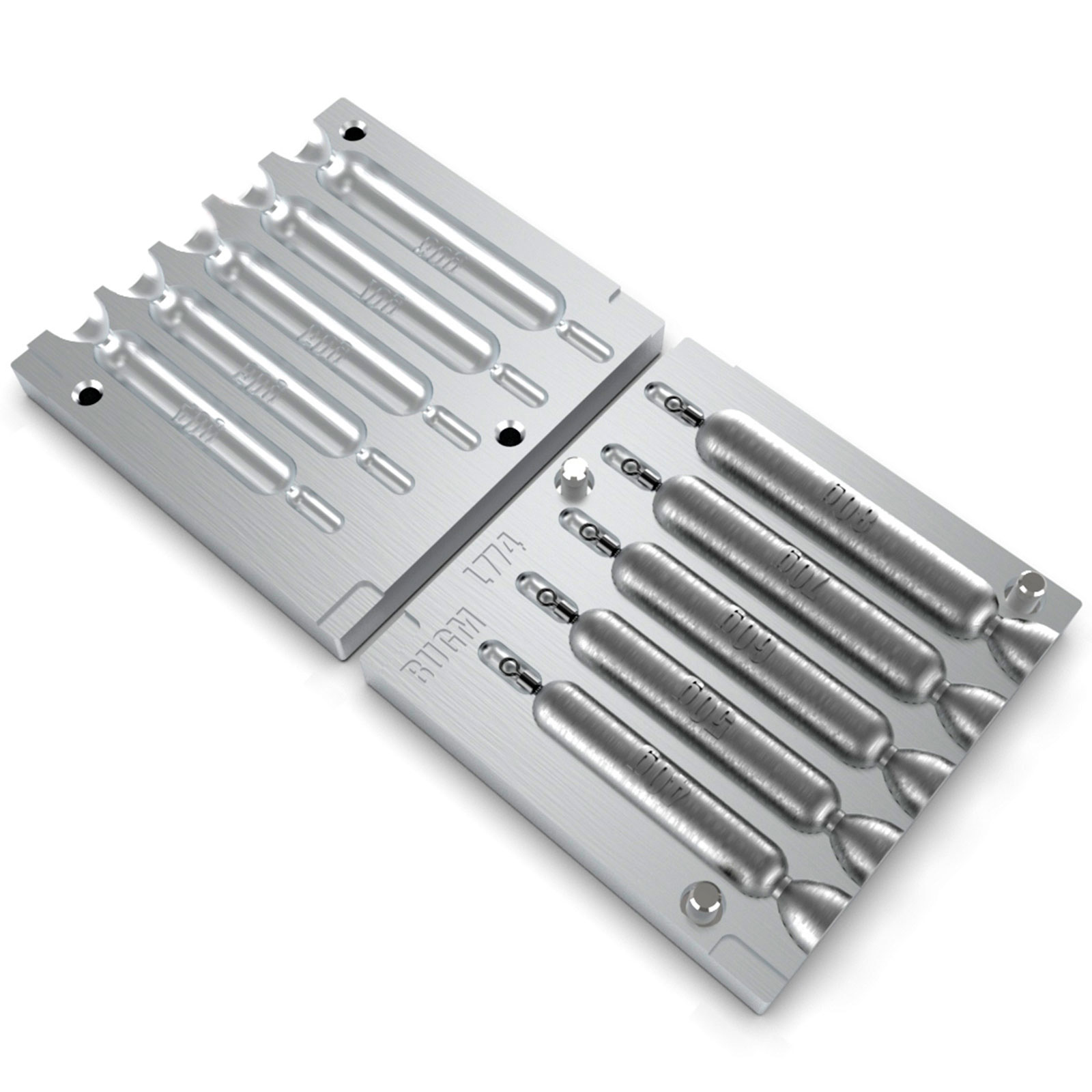
Vacuum forming molds consist of two types of structures:
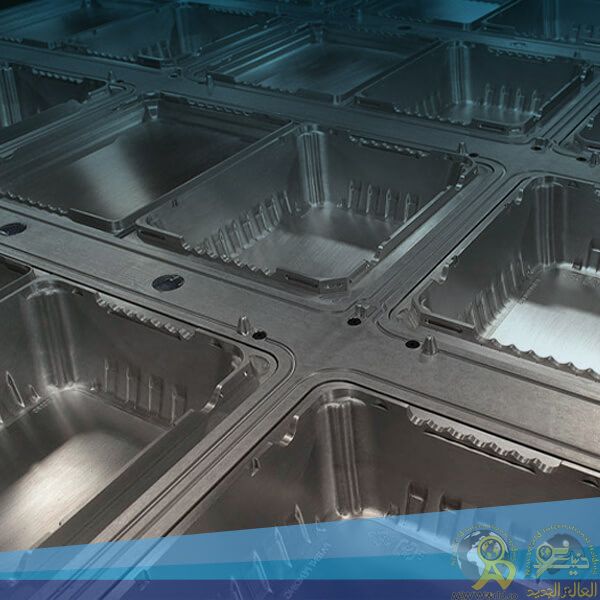
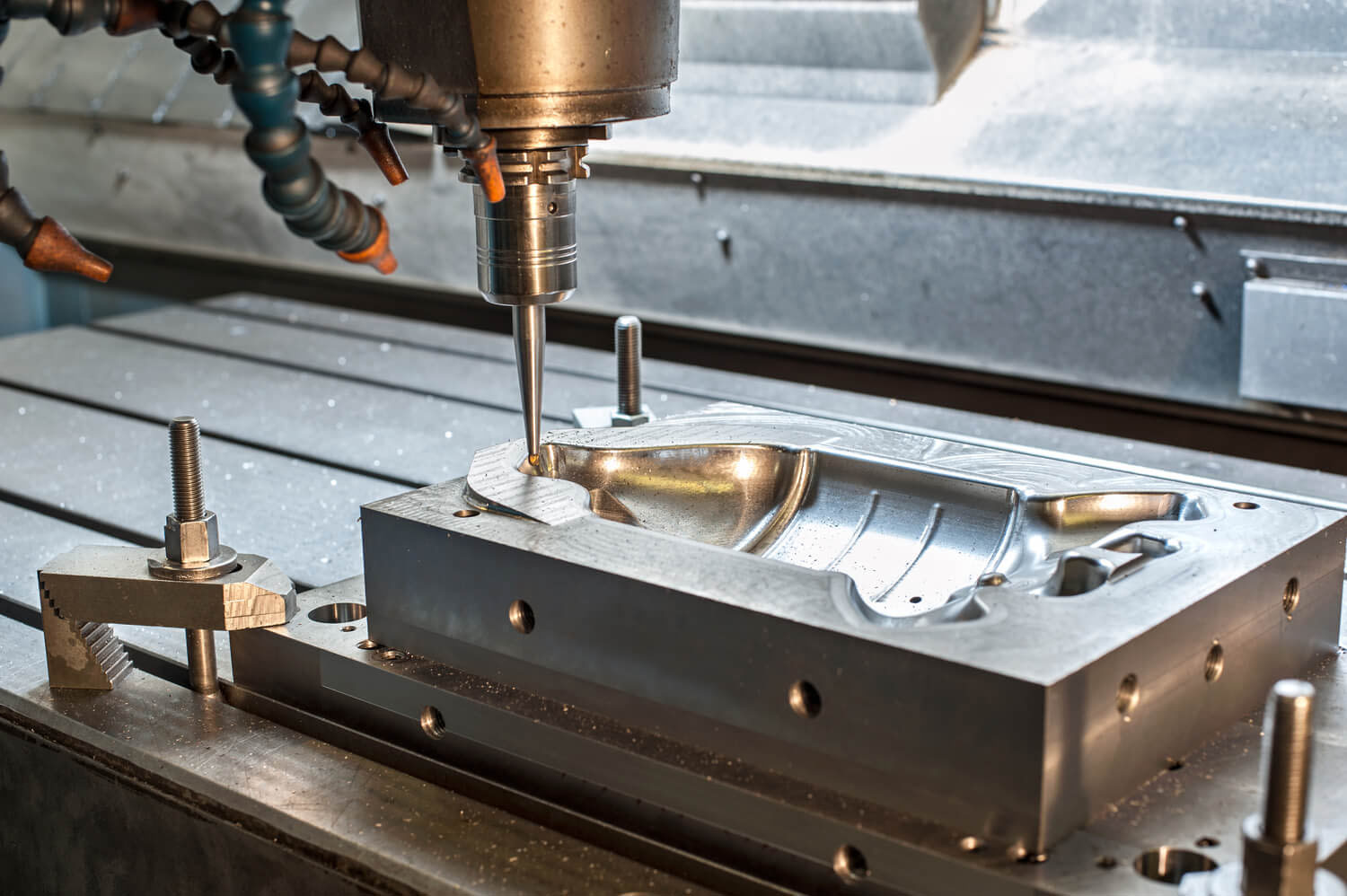
CNC (Computer Numerical Control):
Description: The desired mold is first designed and then crafted on an aluminum sheet using CNC.
High precision and focus in manufacturing.
50% better quality compared to casting methods.
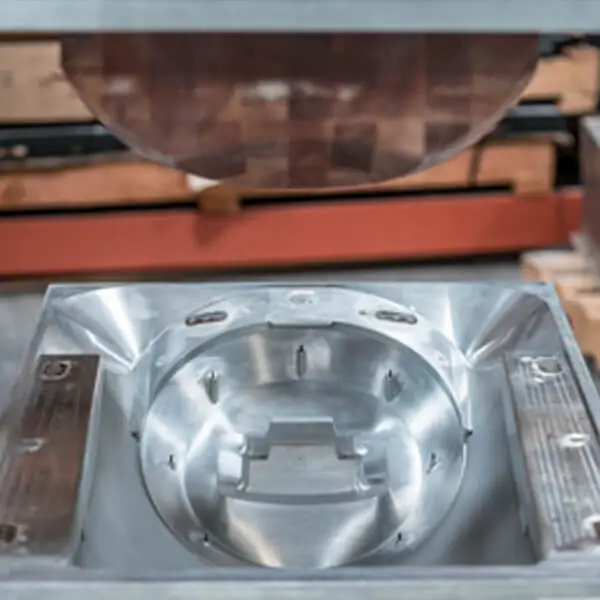
Casting (Lead Molding):
Description: The casting structure includes a wooden model and casting. In this method, molten materials are poured into a sand mold, taking the shape of the sand mold and eventually forming a vacuum mold.
Traditional and common method.
Less precision and focus compared to CNC.
Both vacuum forming mold-making methods have their own specific advantages and disadvantages:
Mold-making using CNC.
-


Advantages:
High Precision: As mentioned, CNC machining offers very high precision, making it suitable for projects that require detailed accuracy.
High Quality: Due to better quality compared to casting methods, higher-quality materials are produced.
Repeatability: The ability to produce a large number of parts with consistent precision.
Disadvantages:
High Cost: The cost of manufacturing using CNC machines is generally higher.
Time-Consuming: Depending on the project, it may take longer to produce a part.
Casting (Lead Molding)
 |  |  |
Advantages:
Fast Production: Suitable for high-volume production of parts.
Lower Costs: In continuous and large-scale production, the cost per unit is lower.
Disadvantages:
Lower Precision: Parts may require additional finishing or other adjustments.
Lower Quality: Compared to the CNC method, the quality of parts may be lower in some cases.
Conclusion:
Both molding methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. The best choice depends on the type of project, budget, and specific production needs. For high precision and superior quality, CNC is the better option, while for high-volume production with lower costs, casting is more suitable.
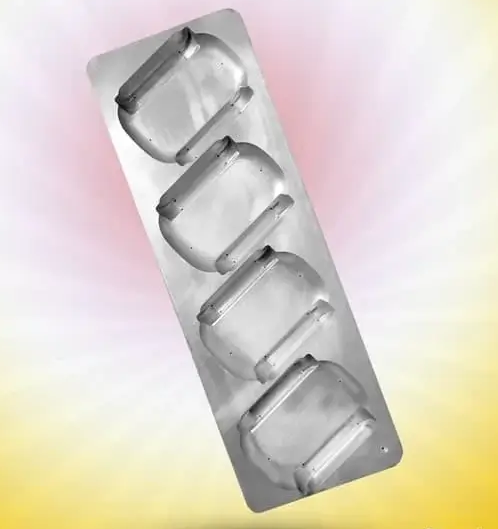
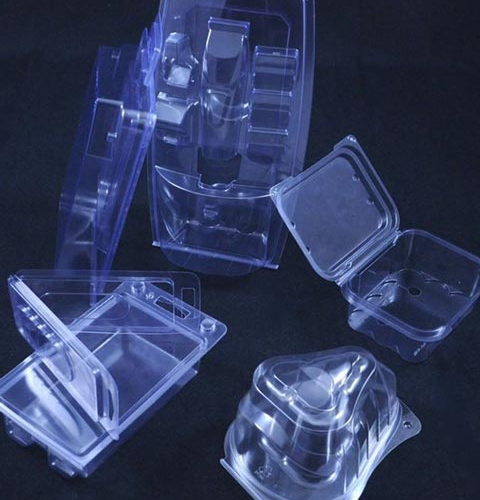
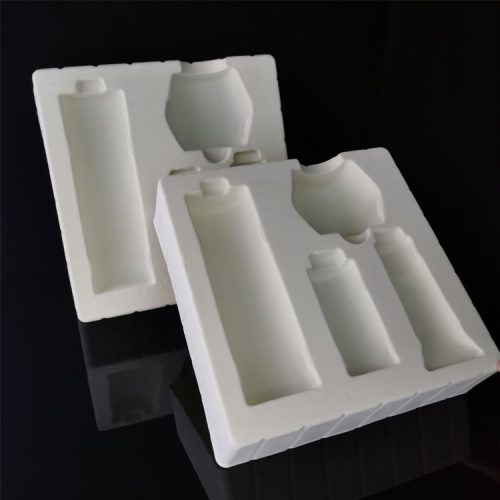



































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.